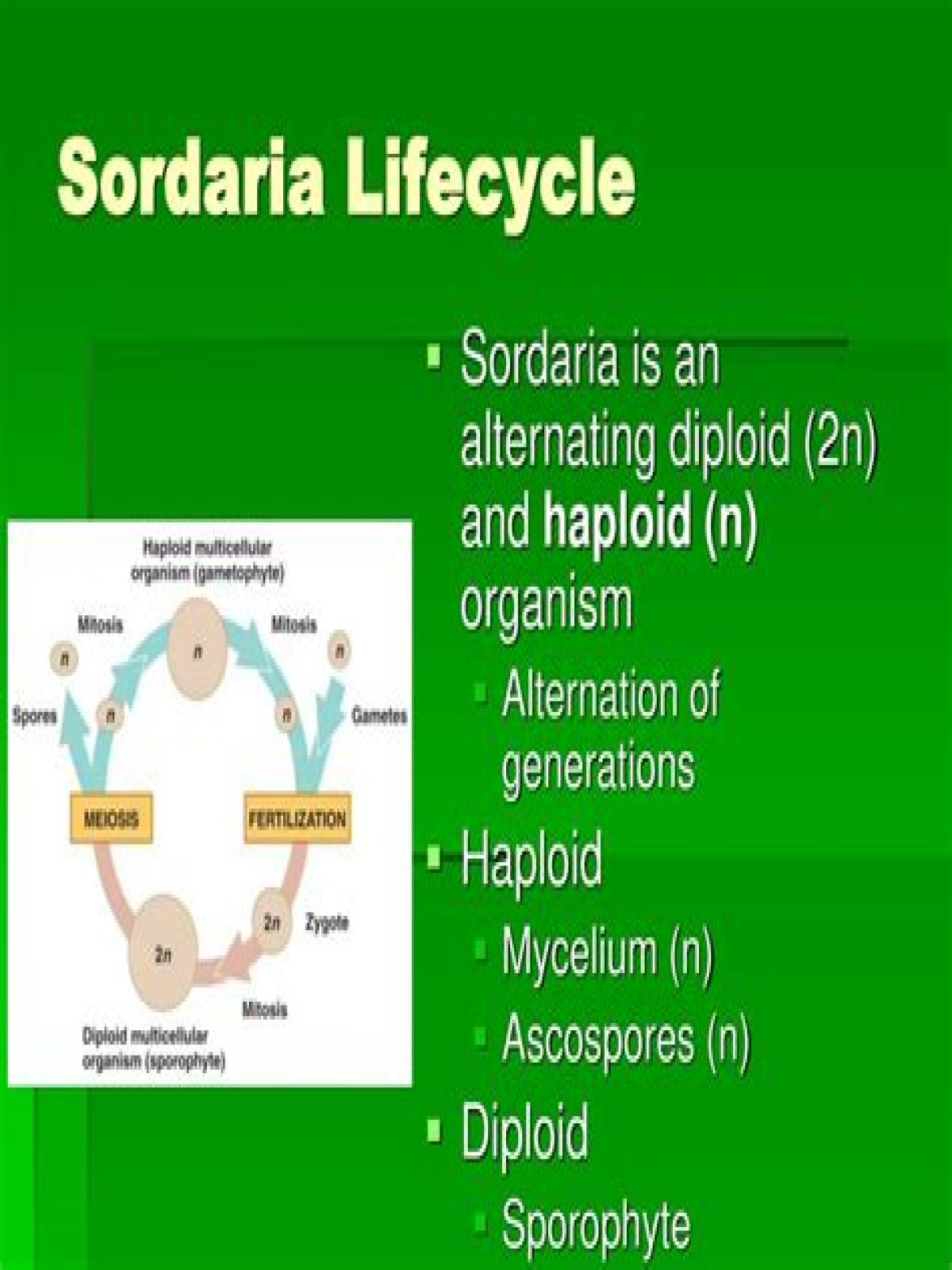
Sordaria is a haploid organism for most of its life cycle. It becomes diploid only when the fusion of the mycelia of two different strains results in the fusion of the two different types of haploid nuclei to form a diploid nucleus. The diploid nucleus must then undergo meiosis to resume its haploid state.
- Are Sordaria haploid?
- How many chromosomes does Sordaria?
- What type of fungi is Sordaria?
- How does meiosis happen in Sordaria?
- What type of life cycle does Sordaria have?
- Which type of cells are produced by meiosis in Sordaria?
- Why is Sordaria an ideal organism for the demonstration of crossing over?
- Is ascospores haploid or diploid?
- Are ascospores produced by meiosis or mitosis?
- Are fungi haploid?
- Can Sordaria cause human disease?
- What type of conditions might affect crossing over in Sordaria?
- Is the initial Sordaria organism haploid or diploid?
- Which of the following is a haploid male cell?
- What type of Ascocarp does Sordaria have?
- Which of these is a Basidiocarp?
- Is Oosphere haploid or diploid?
- Are Ascospores motile?
- What is diploid somatic cell?
- What controls the frequency of crossing over?
- How does crossing over increase genetic variation?
- How is a 4 4 Spore arrangement made?
- What is crossover percentage?
- What is the ploidy of Basidium?
- Why are Ascospores formed?
- What is the ploidy level of the spores produced in the Sporangium?
- Are fungal hyphae diploid or haploid?
- Is fungi multicellular or unicellular?
- What parts of the mushroom Basidiocarp are diploid?
Are Sordaria haploid?
Sordaria is haploid with the chromosome number n=7. Sordaria does not have distinct sexes, but has mating types. During asexual (non-sexual) phase, haploid spores germinate and form haploid hyphae that grow and branch into expanding patchwork called mycelia.
How many chromosomes does Sordaria?
These, in turn, are replicated, so we have eight chromosomes. From top to bottom: two with tan alleles, two with black alleles, two with tan alleles, and two with black alleles.
What type of fungi is Sordaria?
Sordaria fimicola is an ascomycete fungi that can be found growing in rotting vegetation and animal dung (in fact, the name Sordaria fimicola means “filthy dung dweller”). Sordaria and another ascomycete, the common bread fungus Neurospora crassa (Fig.How does meiosis happen in Sordaria?
This sexual reproductive portion of the Sordaria life cycle is called the telomorph life cycle. Through the process of meiosis, a recombination of the genome from “crossing over,” those diploid zygotes develop four haploid nuclei. … These nuclei then undergo their own mitosis. Eight haploid nuclei result from this.
What type of life cycle does Sordaria have?
They all have a short life cycle, usually 7–12 days, and are easily grown in culture. Most species are self-fertile and each strain is isogenic. All kinds of mutants are easily induced and readily obtainable with particular ascospore color mutants.
Which type of cells are produced by meiosis in Sordaria?
Crossing Over during Meiosis in Sordaria Meiosis involves two successive nuclear divisions that produce four haploid cells.
Why is Sordaria an ideal organism for the demonstration of crossing over?
Why is S. fimicola an ideal organism for the demonstration of crossing-over? The fact that it displays both haploid and diploid stages of reproduction allows scientists to easily manipulate different strains of the organism.Is ascospores haploid or diploid?
A diploid ascus that forms in the ascocarp undergoes karyogamy, meiosis, and mitosis to form eight ascospores. A haploid zygote that forms in the ascocarp undergoes karyogamy, meiosis, and mitosis to form eight ascospores.
What is the purpose of the Sordaria lab?The purpose of this investigation is to determine the frequency of meiotic divisions analyzed from hybrid crossings collected from different strains of the fungus Sordaria fimicola. The experiment was conducted to demonstrate hybrid crossings with MI and MII patterns of ascospores within the asci.
Article first time published onAre ascospores produced by meiosis or mitosis?
Ascospores are formed in ascus under optimal conditions. Typically, a single ascus will contain eight ascospores (or octad). The eight spores are produced by meiosis followed by a mitotic division. Two meiotic divisions turn the original diploid zygote nucleus into four haploid ones.
Are fungi haploid?
In the majority of fungi, all structures are haploid except the zygote. Nuclear fusion takes place at the time of zygote formation, and meiosis follows immediately. … Fungi usually reproduce both sexually and asexually. The asexual cycle produces mitospores, and the sexual cycle produces meiospores.
Can Sordaria cause human disease?
The plant disease that we call ergot results. Diseased grain or flour, if consumed, produces ergotism in humans and livestock. Temporary insanity, painful involuntary muscle contractions, gangrene, and death result.
What type of conditions might affect crossing over in Sordaria?
It is investigated how factors such as temperature and ultraviolet light have affected the gene to centromere distance in Sordaria. Results obtained in lab as well as scientific researches prove that as temperatures increases the percent of crossing over increases as well.
Is the initial Sordaria organism haploid or diploid?
Sordaria is a haploid organism for most of its life cycle. It becomes diploid only when the fusion of the mycelia (filament like groups of cells) of two different strains results in the fusion of the two different types of haploid nuclei to form a diploid nucleus.
Which of the following is a haploid male cell?
They are also referred to as sex cells. Female gametes are called ova or egg cells, and male gametes are called sperm. Gametes are haploid cells, and each cell carries only one copy of each chromosome.
What type of Ascocarp does Sordaria have?
Sordaria fimicola: This is an example of a species that does not produce a stroma. In nature, this species grows on dung. Such species are said to be coprophilous. The perithecia are small, black, flask-shaped ascocarps with an ostiole (Fig.
Which of these is a Basidiocarp?
Which of these is a basidiocarp? A mushroom is a basidiocarp.
Is Oosphere haploid or diploid?
Oosphere is the female reproductive cell of certain algae or fungi, which is formed in the oogonium after meiosis, hence it is haploid (n) and when fertilized it becomes the oospore, hence, oospore is diploid (2n).
Are Ascospores motile?
6.11. Fungi from Ascomycota have septate and haploid mycelia and the sexual spores, ascospores, are produced in an ascus on a fruiting body, the ascomata. Typically, eight ascospores are produced in each ascus. No motile zoospores are produced.
What is diploid somatic cell?
A somatic cell is any cell of the body except sperm and egg cells. Somatic cells are diploid, meaning that they contain two sets of chromosomes, one inherited from each parent. Mutations in somatic cells can affect the individual, but they are not passed on to offspring.
What controls the frequency of crossing over?
Because the frequency of crossing over between any two linked genes is proportional to the chromosomal distance between them, crossing over frequencies are used to construct genetic, or linkage, maps of genes on chromosomes. Mutations, temperature changes, and radiation all affect crossing over frequency.
How does crossing over increase genetic variation?
Crossing over is a process that happens between homologous chromosomes in order to increase genetic diversity. During crossing over, part of one chromosome is exchanged with another. … Gametes gain the ability to be genetically different from their neighboring gametes after crossing over occurs.
How is a 4 4 Spore arrangement made?
By observing the order of the ascospores in the ascus one can determine the order in which the chromosomes are segregated (separated) during meiosis. If no crossover events occur, the two genes will segregate during meiosis I and produced a 4:4 arrangement of ascospores.
What is crossover percentage?
About 40 percent of American vehicles sold are crossovers.
What is the ploidy of Basidium?
In the gills of the fruiting body, some cells undergo fusion of these two nuclei. These now diploid cells are the basidia. The diploid phase is very brief. Soon after fusion, meiosis takes place, resulting in four haploid nuclei.
Why are Ascospores formed?
Ascospores are generally found in clusters of four or eight spores within a single mother cell, the ascus. These spores are formed as a means of packaging postmeiotic nuclei. As such, they represent the “gametic” stage of the life cycle in these fungi.
What is the ploidy level of the spores produced in the Sporangium?
The sporophyte is a diploid (2n) spore-producing plant. When reproducing, the sporophyte produces specialized leaves called sporophylls.
Are fungal hyphae diploid or haploid?
The nuclei inside the fungal hyphae are haploid, unlike the diploid cells of most plants and animals. Therefore, fungi don’t have to undergo meiosis before fertilization.
Is fungi multicellular or unicellular?
Fungi can be single celled or very complex multicellular organisms. They are found in just about any habitat but most live on the land, mainly in soil or on plant material rather than in sea or fresh water.
What parts of the mushroom Basidiocarp are diploid?
The hyphae in the gills of basidiocarps contain cells that are dikaryotic. This means the cells contain two nuclei. These dikaryotic cells give rise to basidia, shown in Figure above. Before spores can be produced, the two nuclei in the basidia fuse, making a diploid cell.