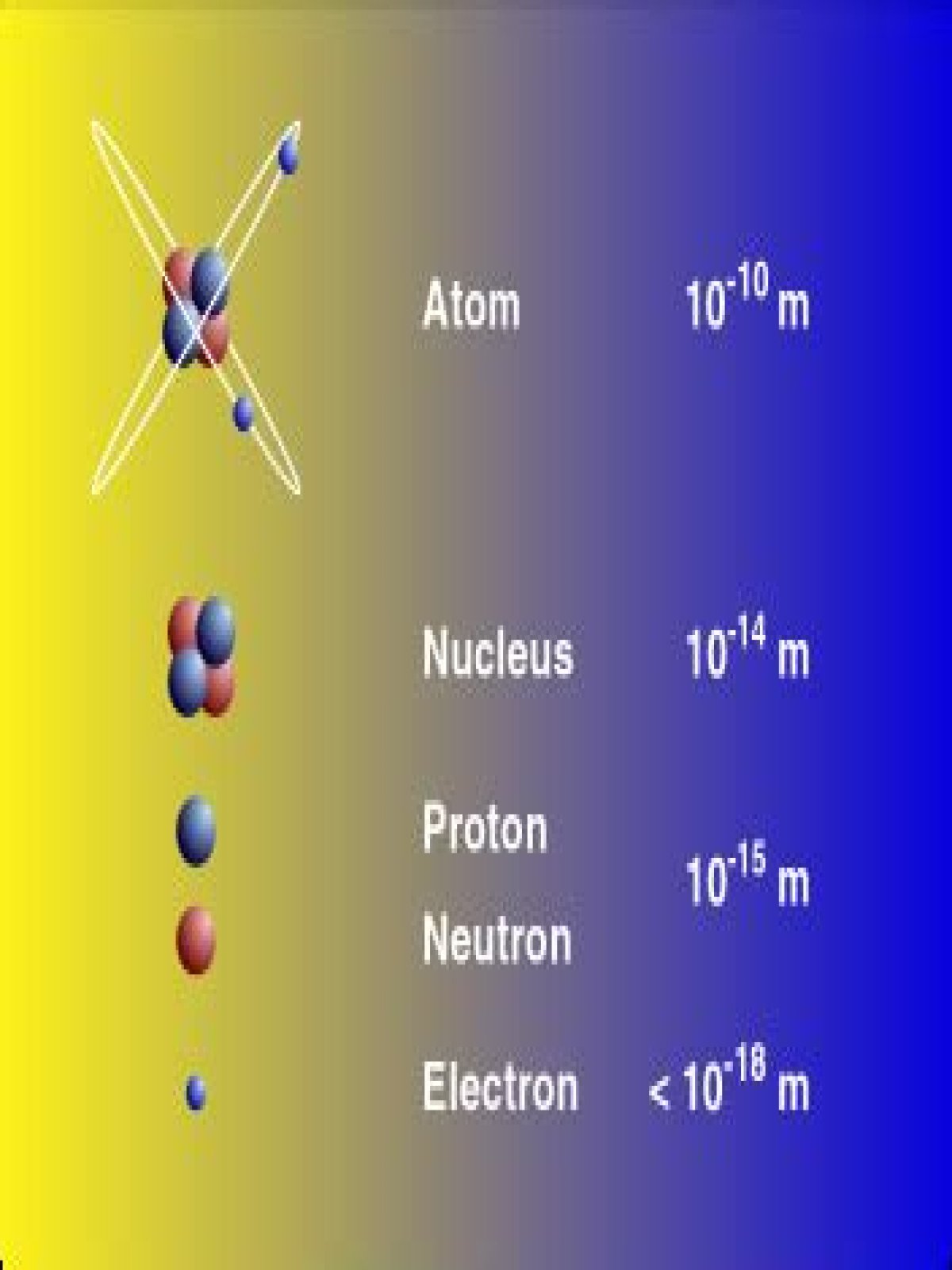
It is concluded that the diameter of the electron is comparable in magnitude with the wave-length of the shortest γ-rays. Using the best available values for the wave-length and the scattering by matter of hard X-rays and γ-rays, the radius of the electron is estimated as about 2 × 10−10 cm.
- What is the diameter of an electron in nanometers?
- What is the diameter of proton?
- Does an electron have a radius?
- Where is the size of an electron?
- What is the size of a proton neutron and electron?
- What is the diameter of a neutron?
- What is the diameter of an atom?
- What is the size of an electron in FM?
- What is the size of a quark?
- What is the diameter of hydrogen?
- What is the diameter of a proton in NM?
- Do electrons have size?
- Do electrons have width?
- How small is the electron?
- How much is the radius of electron?
- What is electron in chemistry?
- Are quark stars real?
- Are electrons the same size as protons?
- What is the diameter of the nucleus?
- How do you find the electrons?
- What is the diameter of a photon?
- Is an electron bigger than a photon?
- What is the size of an electron in amu?
- How do you find the diameter of a nucleus?
- What is the diameter of a typical molecule?
- How do you find electron density?
- How do you calculate electron density?
- Is an electron infinitely small?
- What is the tiniest thing in the world?
What is the diameter of an electron in nanometers?
Electron Radius (classical)Nanometer [nm]0.01 Electron radius (classical)2.81794092E-8 nm0.1 Electron radius (classical)2.81794092E-7 nm1 Electron radius (classical)2.81794092E-6 nm2 Electron radius (classical)5.63588184E-6 nm
What is the diameter of proton?
The team reports that protons measure 0.833 femtometers in diameter (a femtometer is one-trillionth of a millimeter). This measurement is roughly 5% percent smaller than the previously-accepted radius value.
Does an electron have a radius?
The classical electron radius It has a value of 2.82×10-15 m. That’s certainly small. Now compare this with the measured radius of a proton, which is 1.11×10-15 m [3]. … This ratio, 1836, would set the electron’s radius at approximately 12 times smaller than a proton: at 9.1×10-17 m.Where is the size of an electron?
The electron is a fundamental particle,it is very small,the second smallest particle after the neutrino. its size interm of a radius is estimated,not measured, about 10^-16 cm., therefore no exact number ,it has rest mass so it occupies certain space size,but this size is too small be measured exactly today.
What is the size of a proton neutron and electron?
Protons, neutrons, and electrons: Both protons and neutrons have a mass of 1 amu and are found in the nucleus. However, protons have a charge of +1, and neutrons are uncharged. Electrons have a mass of approximately 0 amu, orbit the nucleus, and have a charge of -1.
What is the diameter of a neutron?
A neutron also has about the same diameter as a proton, or 1.7×10−15 meters.
What is the diameter of an atom?
the diameter of an atom is typically around 0.1 nm or 1 × 10 -10 m. the thickness of a piece of paper is typically around 0.05 mm or 5 × 10 -5 m. therefore, a piece of paper is about half a million atoms thick.What is the size of an electron in FM?
Electron Radius (classical)Femtometer [fm]0.1 Electron radius (classical)0.281794092 fm1 Electron radius (classical)2.81794092 fm2 Electron radius (classical)5.63588184 fm3 Electron radius (classical)8.45382276 fm
How dense is an electron?Dividing the electron mass, 10-27g, by the (very loosely estimated) volume ~ 10-48cm, one gets the density 1021g/cm3.
Article first time published onWhat is the size of a quark?
While the size of protons and neutrons is of the order of a Fermi (10−15 m), the size of quarks is ~10−18 m. It is deemed that quarks are composed of smaller particles – preons.
What is the diameter of hydrogen?
Question: A hydrogen atom has a diameter of approximately 1.06×10−10 m 1.06 × 10 − 10 m , as defined by the diameter of the spherical electron cloud around the nucleus. The hydrogen nucleus has a diameter of approximately 2.40×10−15 m 2.40 × 10 − 15 m .
What is the diameter of a proton in NM?
Bibliographic EntryResult (w/surrounding text)Standardized ResultWorld Book Encyclopedia. Chicago: World Book, 1998: 69.”A proton has a diameter of approximately one-millionth of a nanometer“10−15 m
Do electrons have size?
Electrons do not have a size. Electron interactions have size.
Do electrons have width?
electrons have mass, but at the resolution limits of our current technology they appear to have no size i.e., they are like mathematical points.
How small is the electron?
An electron itself is small (its size is not known, but we do know that it is smaller than a nucleus), but it occupies the space of the atom by constantly whirling around in a kind of orbit around the nucleus. 10-15 m in radius.
How much is the radius of electron?
The classical electron radius is well known and effectively represents the charge radius which is 2.82 X 10^-15 m.
What is electron in chemistry?
If you take chemistry, you will learn about electrons. Electrons are the smallest of the particles that make up an atom, and they carry a negative charge. The number of protons and electrons is equal in a neutral atom. The hydrogen atom, for example, has just one electron and one proton.
Are quark stars real?
There is currently no strong evidence that quark stars exist; however, some observations suggest they may. For example, scientists using data from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory reported that the nearby neutron-star candidate RX J1856.
Are electrons the same size as protons?
Electrons are tiny compared to protons and neutrons, over 1,800 times smaller than either a proton or a neutron. Electrons are about 0.054% as massive as neutrons, according to Jefferson Lab.
What is the diameter of the nucleus?
The size (diameter) of the nucleus is between 1.6 fm (10−15 m) (for a proton in light hydrogen) to about 15 fm (for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium). These sizes are much smaller than the size of the atom itself by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).
How do you find the electrons?
- The number of protons in the nucleus of the atom is equal to the atomic number (Z).
- The number of electrons in a neutral atom is equal to the number of protons.
What is the diameter of a photon?
A photon is in shape like a thin stick if its energy is lower than the rest energy of an electron and like a plate if its radius is smaller than the classical radius of an electron. For a photon of hν=13.6 eV, the photon radius is 34.9 pm and is less than the Bohr radius.
Is an electron bigger than a photon?
the size of photons and electrons are same as mass,but electron is negatively charged particle and photon is the energy (quanta).
What is the size of an electron in amu?
Electrons have a mass of approximately 0 amu, orbit the nucleus, and have a charge of−1.
How do you find the diameter of a nucleus?
The average radius of a nucleus with A nucleons is R = R0A1/3, where R0 = 1.2*10-15 m. Details of the calculation: R = (1.2*10-15 m)*(56)1/3 = 4.6*10-15 m. diameter = 2R = 9.2*10-15 m.
What is the diameter of a typical molecule?
The diameter of a molecule, assuming it to be spherical; has a numerical value of 10-8 centimeter multiplied by a factor dependent on the compound or element. Gases with a larger molecular diameter diffuse slower across the prepared membrane [21-23].
How do you find electron density?
- Double and triple bonds count as ONE REGION OF HIGH ELECTRON DENSITY.
- An unpaired electron counts as ONE REGION OF HIGH ELECTRON DENSITY.
How do you calculate electron density?
Free Electron Density in a Metal will have free electron density n = x10^ /m3. will have a number of atoms per unit volume n’ = x10^ /m3. The number of atoms per unit volume multiplied by the number of free electrons per atom should agree with the free electron density above.
Is an electron infinitely small?
When interacting like a particle, an electron is exactly a single point in space and has no shape according to the Standard Model, as shown in this illustration. … This means that the electron’s mass is not literally squeezed into an infinitely small volume.
What is the tiniest thing in the world?
Protons and neutrons can be further broken down: they’re both made up of things called “quarks.” As far as we can tell, quarks can’t be broken down into smaller components, making them the smallest things we know of.